Tasks
A task includes a group of permissions for functionality, such as records and lists, in a feature area.
Tasks and permissions work together to determine the level of control for a task. For example, you can enable a user to view data without the ability to add or edit data; data management is the task, and view, add, and edit are the permissions. For more information, see Permissions.
You manage tasks in one of two ways:
-
To provide full access, select tasks that appear by default based on your organization's capabilities.
-
To limit access, combine tasks and permissions to determine security.
Tip: New to security? To understand feature areas, their roles, and how the level of access is determined for a user, see Role-based Security Overview.
When you create or edit a role, the feature area's tasks appear by default.
Tip: The tasks that appear depend on the capabilities your organization uses. You can't add, edit, or remove these.
To provide full access to a task, select the task. All of its permissions select automatically.
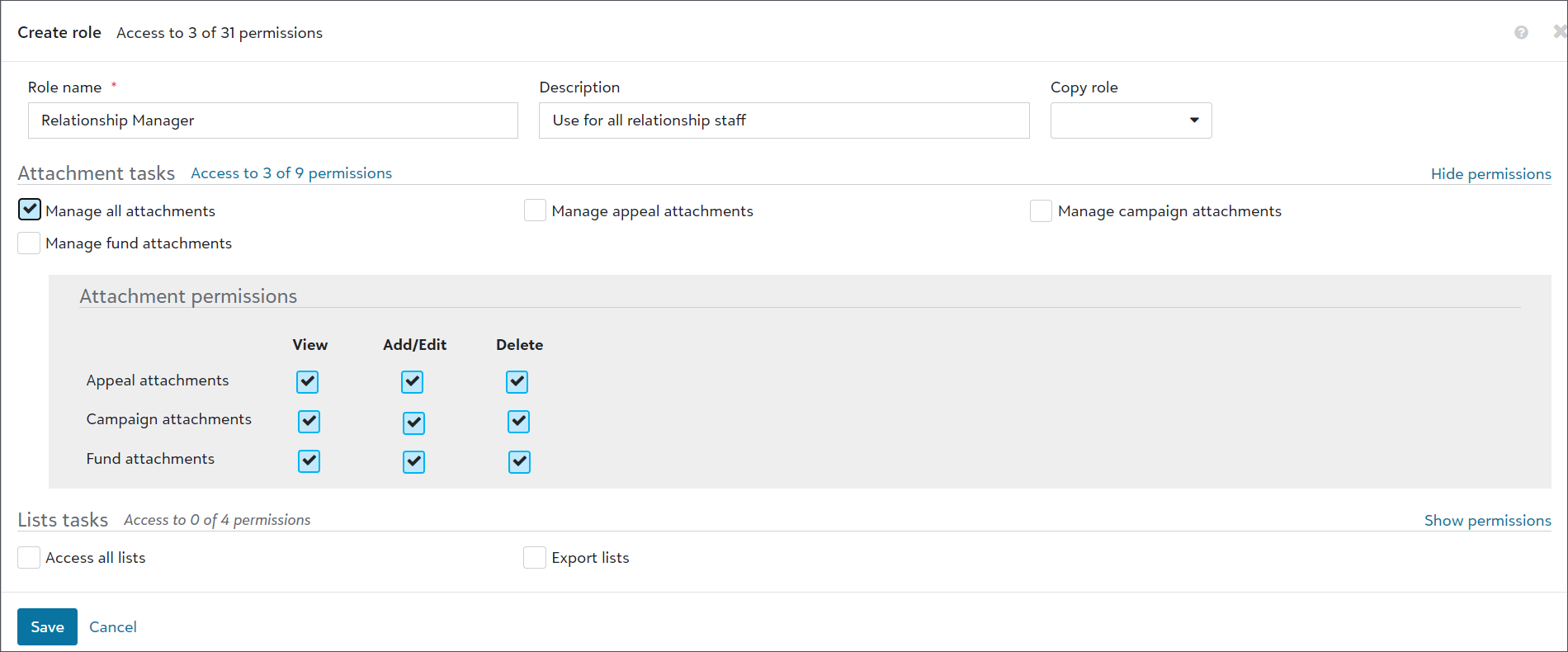
When you create or edit a role, the feature area's tasks and permissions appear by default.
Tip: The tasks and permissions that appear depend on the capabilities your organization uses. You can't add, edit, or remove these.
To limit what the role can do by combining tasks and permissions, select the task you want to provide full access for, and then select individual permissions for the other task to limit its access.
For example, select Manage Task A to provide full access to it. To limit access to Task B, select Show permissions. Then, select its Add/Edit permission. This provides users in the role with full access to Task A, but only with add and edit rights to Task B. They can't delete data for Task B. For more information, see Permissions.
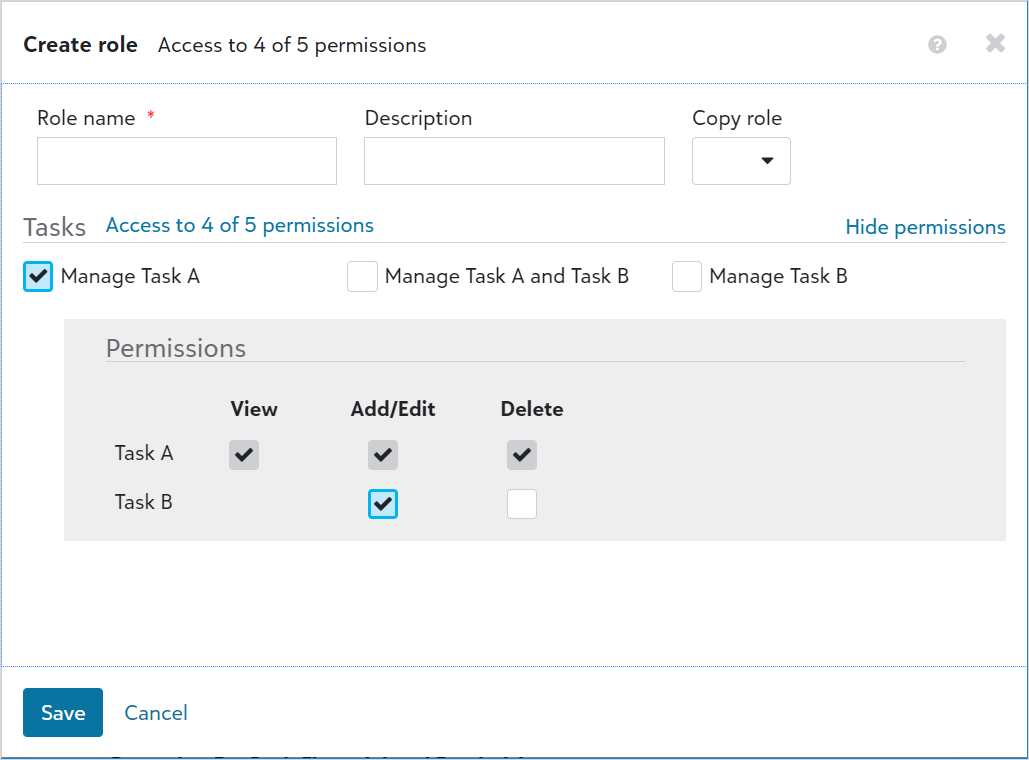
Tip: To provide a way for you to easily adjust and change individual permissions as needed, the checkbox for a task permission doesn't select automatically when you select all of its individual permissions.
To apply a task to a user, assign them a role with access to it. For more information, see Roles.
Tip: What's next? Permissions